You have choices, make the right choice
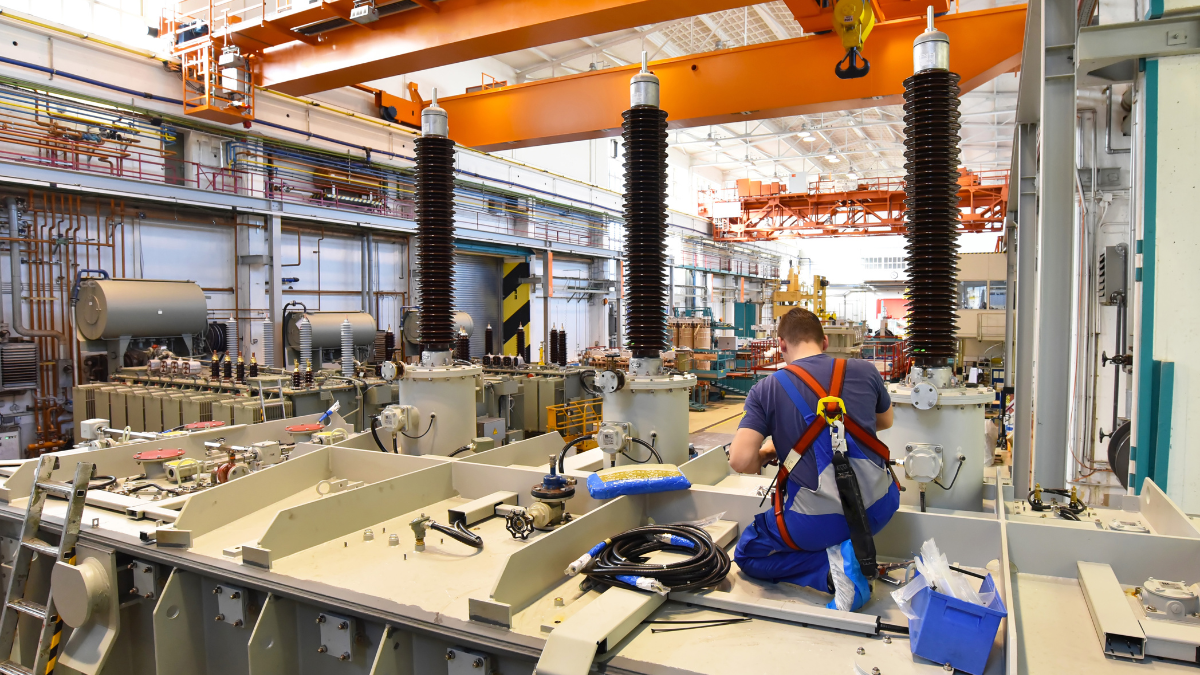

How GD&T Improves Manufacturing Efficiency and Reduces Costs
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) has transformed the way manufacturers communicate design intent and product specifications.
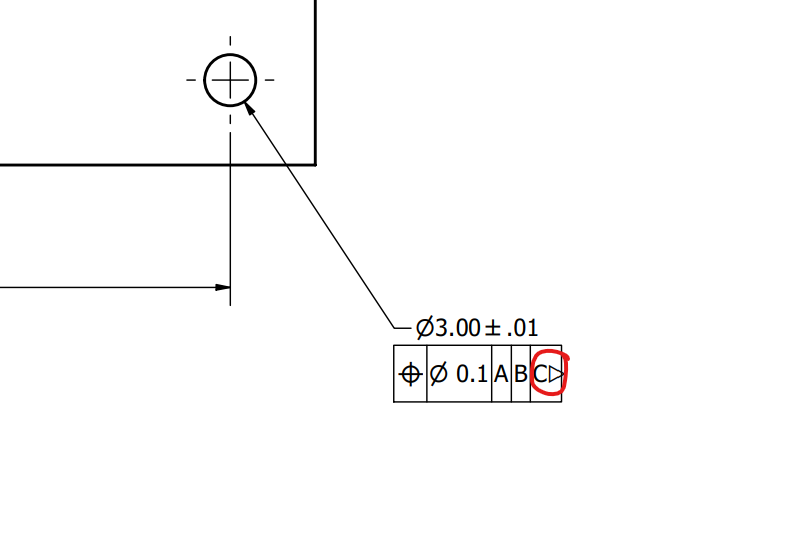
Enhancing Datum Reference Frames in GD&T: Blending Translation Modifiers and Rotational Freedom
Governed by standards such as ASME Y14.5, GD&T uses datums—theoretically exact references derived from physical features—to establish datum reference frames (DRFs) that constrain a part’s six degrees of freedom (DOF): three translational (x, y, z) and three rotational (u, v, w).
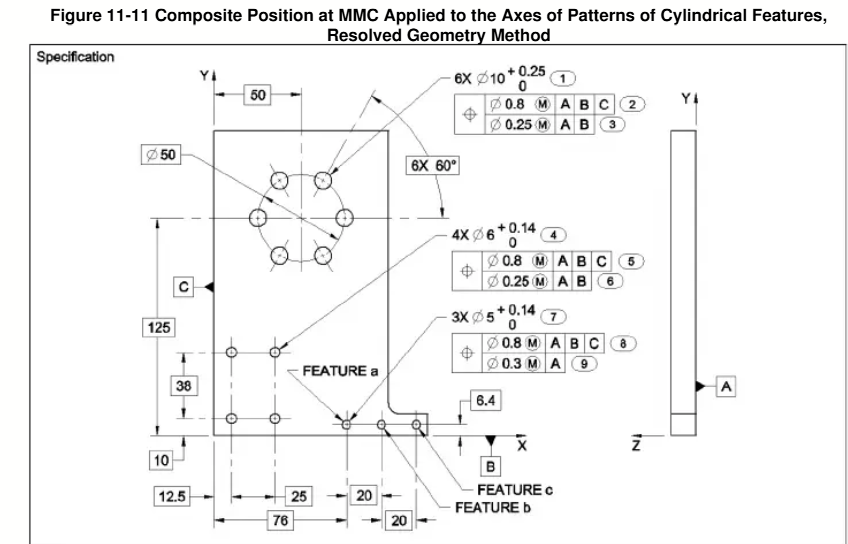
ASME Y14.45-2021 Compliance Mandate: Exclusion of Characteristic Identifiers from Basic Dimensions
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Y14.45-2021 standard, Measurement Data Reporting, establishes uniform and authoritative practices for documenting inspection results derived from engineering product definitions.
Anchoring Precision: Advanced Metrological Strategies for Primary Datum Plane Establishment on Coordinate Measuring Machines
The integrity of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) specifications hinges entirely upon the stability and accuracy of the Datum Reference Frame (DRF). As the foundation of this framework, the primary datum plane—typically designated Datum A—serves the critical function of establishing the initial orientation and location of a manufactured component in three-dimensional space.
